Archive for the ‘China’s Intangible Cultural Heritage’ Category
Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Museum
 The Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Museum was established in the spring of 1953 in the People’s Park in Urumchi City. A new museum was later built in 1962 at a new site on Xibei Lu. The building occupies a space of 11,000 square meters and is built in a modern style enhanced by local architectural features. The central dome is thirty meters high and from its height one can view the entire city of Urumchi.
The Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Museum was established in the spring of 1953 in the People’s Park in Urumchi City. A new museum was later built in 1962 at a new site on Xibei Lu. The building occupies a space of 11,000 square meters and is built in a modern style enhanced by local architectural features. The central dome is thirty meters high and from its height one can view the entire city of Urumchi.
The Silk Road derived its fame from silk. The Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region Museum has also become famous for its rich collections of silk artifacts from many periods of history. Brocades from Eastern Han are highlighted, as well as all kinds of specialized silk-woven items from the height of the Tang. These are as lustrous and beautiful today as when they were new and display weaving techniques that were highly refined many hundreds and even thousands of years ago. These are regarded as unique treasures by textile authorities and art historians around the world. A number of the articles on display here are the earliest extant examples of certain weaving technologies in China.
The Xinjiang Autonomous Region has long been a crossroads for many different kinds of people. Their diversity of scripts and cultures is exhibited in this museum through archaeological material, including documents in some twelve different scripts with a particularly large number from the Han-dynasty finds at Turfan. The documents cover military, economic, cultural, and political affairs. Clay or terracotta sculptures are also featured in the Xinjiang Museum. Among these are single-humped Central Asian camels, fat and vigorous Yuan-dynasty horses, women figurines in all postures, impressively fierce soldiers, and so on. These were sculpted in a most natural and vigorous way and have been preserved as a result of Xinjiang’s arid climate. The Xinjiang Museum has several dozen original Tang-dynasty paintings. Although these are not from the hands of famous painters, they still exhibit the vital Tang spirit. They include such subjects as women playing weiqi go or Chinese chess, children frolicking, ‘eight steeds,’people dancing and so on. Other items in the collections include microliths, silver works of art, stone stelaes, coins and currency, ceramics, wooden articles. Of particular note are various foods from the Tang dynasty which, through the arid conditions, have been preserved over the passage of more than one thousand years.
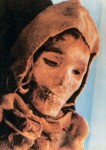
In a similar vein, certain dessicated human corpses, called mummies although they were not treated with chemicals, are kept in the Xinjiang Museum. Some of these date back to 4,000 years ago. They are the earliest known such examples in China and are important in the study not only of humankind but of ethnic composition in this region at the time. Also in the museum are an Eastern-Han couple, buried together and well preserved, and a corpse from the Tang dynasty with well preserved skin and hair.
Presently, the museum opened new exhibits called the Xinjiang History Exhibition and the Xinjiang People’s Customs Exhibition. The history exhibit shows the history of Xinjiang by using material from its rich collections and highlighting material from recent archaeological discoveries. The Customs exhibition introduces the customs and cultural lifestyles of twelve different ethnic groups in Xinjiang, including the Uighur, Kazakh, Mongolian, Kirgiz, Hui, Tajik, Uzbek, Russian, Tatar, Daur, Xibo, and Manchu.
Address: Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region, Urumchi, Xibei Road, #132
Mote info about China’s Museum, please visit here:
Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Museum
This museum was founded on the occasion of the tenth anniversary of the establishment of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, in 1957. The building, expressive of local minority characteristics, is located at the intersection of Xinhua Dajie and Zhongshan Lu in the heart of Hohhot City, the capital of the autonomous region.
Hunan’s 16 Intangible Cultural Heritage Items to Perform in Beijing in March
As a part of the gathered performance activity of Chinese ethnic  intangible cultural heritage items, the reporting performance themed with “Hunan Flavor” was conducted at the Hunan Concert Hall on the evening of March 13. It is reported that Hunan’s 16 ethnic intangible cultural heritage items will be performed in the Beijing Tianqiao Theater on 17 and 18 this month.
intangible cultural heritage items, the reporting performance themed with “Hunan Flavor” was conducted at the Hunan Concert Hall on the evening of March 13. It is reported that Hunan’s 16 ethnic intangible cultural heritage items will be performed in the Beijing Tianqiao Theater on 17 and 18 this month.
Sponsored by the Ministry of Culture and the Ethnic and Religious Affairs Commission, this performance activity was held in Beijing on February 17 and will last until March 30. The ethnic folk artists from different provinces, cities, and autonomous regions across the country will present nine performances for the local audience. Among them, special performances will be made by Hunan, Qinghai, Sichuan and Guizhou provinces, and Tibet, Inner Mongolia and Guangxi Zhuang autonomous regions.
Nearly 200 Hunan-based actors from Xiangxi, Huaihua, Zhangjiajie, Shaoyang, and Yongzhou attended the performance, including Tian Longxin and Dai Bisheng, and Chen Shida, representative heirs of the state-level and provincial-level intangible cultural heritage respectively. The performance displays the colorful folk culture of Hunan’s ethnic minorities with their dances, instrumental music, folk songs, clothing, and so on.
Translator: Lv Xuefen